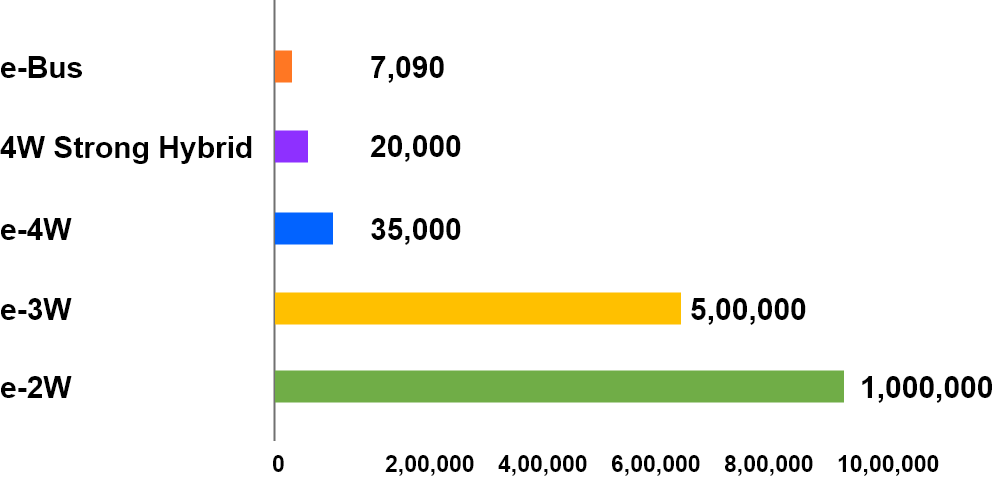National Electric Mobility Mission Plan

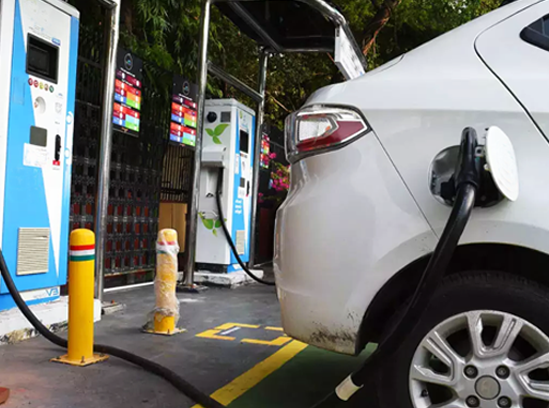
Government of India launched the National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP) 2020 in year 2013. It aims to achieve national fuel security by promoting hybrid and electric vehicles in the country. There is an ambitious target to achieve 6-7 million sales of hybrid and electric vehicles year on year from year 2020 onwards. Government aims to provide fiscal and monetary incentives to kick start this nascent technology.
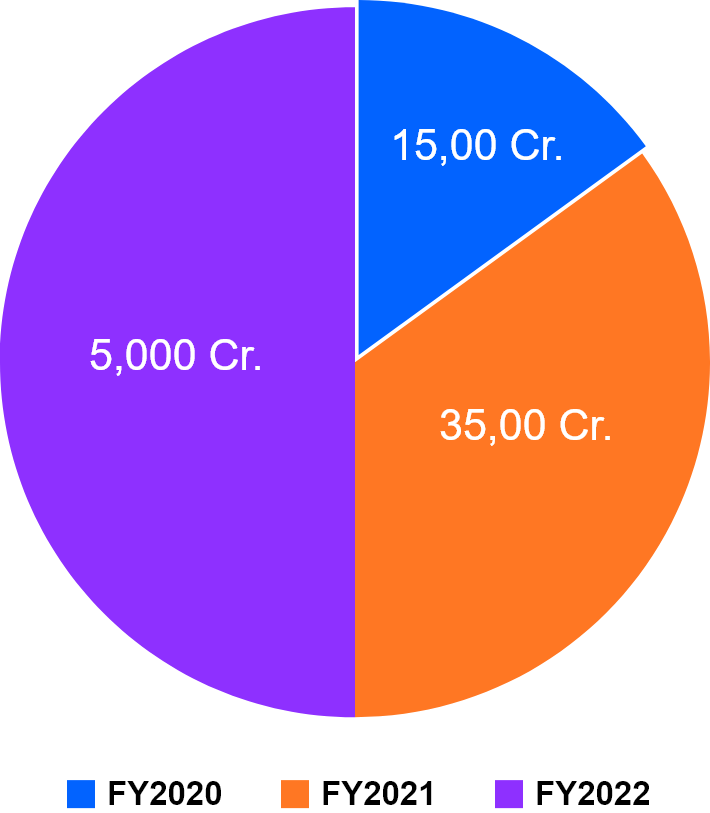
With the support from the Government, the cumulative sale is expected to reach 15-16 million by year 2020. It is expected to save 9500 million litre of crude oil equivalent to saving INR 62000 Cr. It is envisaged that early market creation through demand incentive, in-house technology development and domestic production will help industry reach a self-sufficient economy of scale in the long run by year 2020.

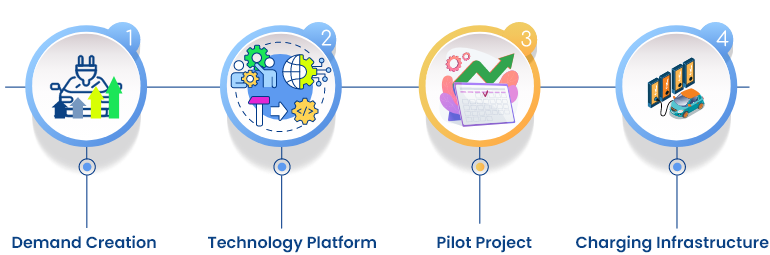
Under NEMMP, Government plans to incentivize buyers of hybrid and electric vehicles. The incentive shall be administered through an efficient and effective electronic mechanism/portal for incentive disbursement. Under this mechanism the manufacturer will reduce the purchase price of a hybrid and electric vehicle (the purchase price will be reduced by the level of the eligible predetermined incentive amount) at the time of selling to the buyer, and the same will be reimbursed to them by the Government.