
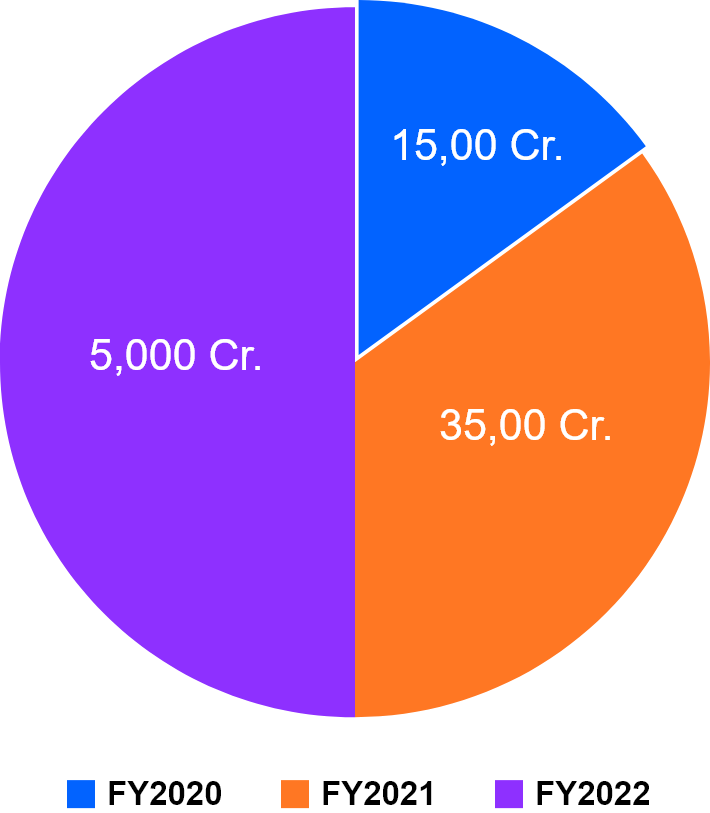
Total fund requirement for this scheme is INR 10,000 crores over three years from 2019-20 to 2021-22, extended till 31st March 2024
The main objective of the scheme is to encourage faster adoption of electric and hybrid vehicle by way of offering upfront incentive on purchase of Electric Vehicles and by way of establishing a necessary charging infrastructure for EVs and carrying out various awareness activities. The scheme will help in addressing the issue of environmental pollution and fuel security. The scheme aims to deploy around 15.62 lakhs EVs across all vehicle categories. The category wise vehicle numbers are provided in below chart
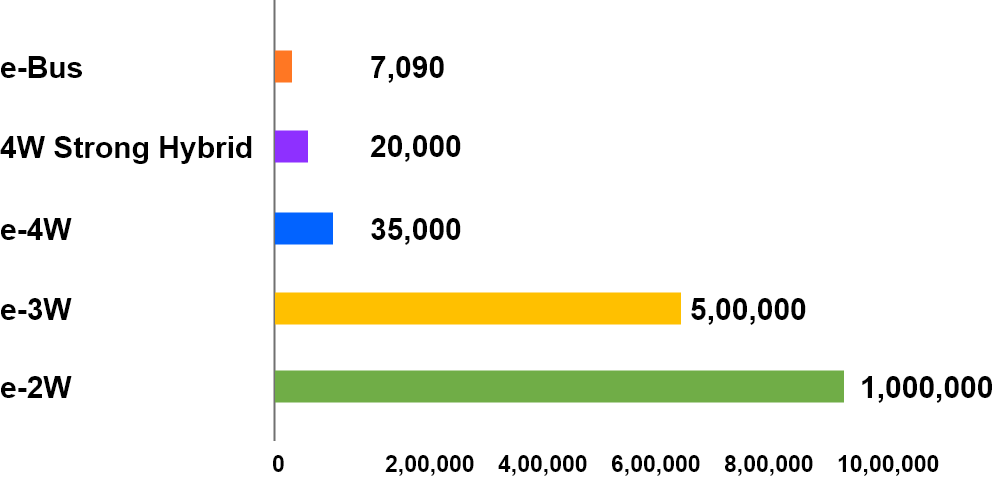

To update regarding progress of FAME India Scheme, Department of Heavy Industries have launched an interactive dashboard. The dashboard provides deployment status of EVs including e-buses and public charging stations under FAME India Scheme Phase I and Phase II.
DashboardTo remove the inferior quality products from the market and promote indigenous development of EVs and its components in India, Government of India launched Phased Manufacturing Program (PMP) with the objective of domestic manufacturing of EVs, its assemblies / sub-assemblies, and parts / sub-parts. Under this scheme, Government aims to provide manufacturing base in India for various EV components like battery packs, lithium-ion cells, AC / DC charger, motor and motor controller, power control unit, etc. Additionally, Government has also approved Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for manufacturing of Advance Chemistry Cell (ACC) to reduce import dependence on ACC batteries. Under PLI Scheme, National Programme on Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) Battery Storage has been developed. The scheme foresees setting up of a cumulative ACC manufacturing capacity of 50 GWh for ACCs and an additional cumulative capacity of 5 GWh for Niche ACC Technologies, with a budgetary outlay of INR 18,100 crore .
